
How to Use an Adjustment Note to Record Bank Fees in Quickbooks
 Did your bank charge you a fee for a customer’s payment? If so, you’ll need to record it. Customers can’t predict whether or not banks will charge you a fee. Maybe the customer made a wire transfer, in which case your bank added a fee to your account. Regardless, it’s important to record fees such as this so that they don’t throw off your financial records. Fortunately, you can easily record bank fees in Quickbooks by using an adjustment note.
Did your bank charge you a fee for a customer’s payment? If so, you’ll need to record it. Customers can’t predict whether or not banks will charge you a fee. Maybe the customer made a wire transfer, in which case your bank added a fee to your account. Regardless, it’s important to record fees such as this so that they don’t throw off your financial records. Fortunately, you can easily record bank fees in Quickbooks by using an adjustment note.
Create a New Expense Account
To get started, log in to Quickbooks and create a new expense account. From the “Accounting” menu, choose “Chart of Accounts,” followed by “New.” Next, select the option to create a new expense account. After giving the expense account a memorable name, such as “bank fees,” click “Save” to complete the setup.
Create a Product
Now it’s time to create a product. Click the gear icon in the corner of Quickbooks Online and choose “Products and Services.” From there, click “New” and choose “Product,” after which you’ll have to give a name. Finally, add the new product to the expense account created in the previous step. You can then click “Save” to finish creating the product.
Create an Adjustment Note
With the expense account and product created, you can proceed to create an adjustment note. An adjustment note, of course, is a type of memo that adjusts the balance of an invoice. When you are charged a bank fee — or other unexpensed fee associated with a transaction — you can use an adjustment note to record it.
To create an adjustment note, click the (+) icon in Quickbooks Online and choose “Adjustment Note.” Next, select the option for “Customer” and choose the product that you created in the previous step. You can then add the amount of the bank fee to your adjustment fee. If your bank charged you for $15, for instance, enter $15 in the amount field.
Connect Adjustment Note to Invoice
The final step involves connecting the adjustment note to the customer’s invoice. This is done by clicking the “Sales” menu, selecting “Customers” and choosing the invoice from which you incurred the bank fee. After selecting “Make Payment,” you can connect the adjustment note to the invoice. Simply untick the box so that Quickbooks recognizes the fee as originating from the invoice.
Have anything else that you’d like to add? Let us know in the comments section below!

What Are the 3 Hosting Modes in Quickbooks Desktop?
 Quickbooks Desktop supports several different hosting modes. These modes determine which computers or devices can access the software from its location. Quickbooks Desktop, of course, is the locally installed version of Intuit’s popular accounting software. It’s not located on the cloud. Rather, it’s installed locally. When using Quickbooks Desktop, though, you might be wondering which hosting mode to choose. Below is a comparison of the three different hosting modes and how they work.
Quickbooks Desktop supports several different hosting modes. These modes determine which computers or devices can access the software from its location. Quickbooks Desktop, of course, is the locally installed version of Intuit’s popular accounting software. It’s not located on the cloud. Rather, it’s installed locally. When using Quickbooks Desktop, though, you might be wondering which hosting mode to choose. Below is a comparison of the three different hosting modes and how they work.
#1) Not Hosting
In “Not Hosting” mode, Quickbooks Desktop is executed in Windows as a traditional process. “Not Hosting” mode allows users to access files via a database server while also leveraging shared computer memory.
It’s important to note that “Not Hosting” mode doesn’t allow for multi-user operation. If you need to set up Quickbooks Desktop with multiple users, you’ll have to choose a different hosting mode. “Not Hosting” mode only supports single-user operation, making it somewhat restrictive in terms of functionality, especially for large businesses with multiple accountants.
#2) Local Files Only
A second hosting mode supported by Quickbooks Desktop is “Local Files Only.” In this mode, Quickbooks Database Server Manager will execute as “QuickBooksDBXX.” You won’t have to manually launch it. As long as your computer is turned on and running, the “QuickBooksDBXX” will run in the background.
Unlike “Not Hosting” mode, “Local Files Only” mode does support multi-user operation. In other words, other users — such as an accountant — can access Quickbooks Desktop remotely. Quickbooks Desktop will still be installed locally on your computer, but other users will be able to connect to your computer over a TCP/IP connection. Keep in mind, though, that “Local Files Only” mode restricts file hosting to the files located on your computer. You can’t use this mode to host files locally elsewhere.
#3) Local and Remote Files
Finally, there’s “Local and Remote Files” hosting mode available in Quickbooks Desktop. In “Local and Remote Files” mode, Quickbooks Database Server Manager is executed as a normal process. The difference is that it only runs when you are logged in to as a Windows user. Once you log in to Windows, it will execute. When you log out of Windows, on the other hand, Quickbooks Database Server Manager will stop running. “Local and Remote Files” mode for Quickbooks Desktop supports multi-user operation using the same technology as “Local Files Only” mode.
Have anything else that you’d like to add? Let us know in the comments section below!

How to Fix Misaligned Documents Printed Quickbooks
 Are your paychecks, invoices or other documents printed in Quickbooks misaligned? Because these documents are a representation of your business, you shouldn’t use them if they are misaligned. They may contain all the necessary information, but they’ll create a poor brand image for your business. Fortunately, you don’t have to replace your printer. Instead, you can adjust the alignment of your existing printer.
Are your paychecks, invoices or other documents printed in Quickbooks misaligned? Because these documents are a representation of your business, you shouldn’t use them if they are misaligned. They may contain all the necessary information, but they’ll create a poor brand image for your business. Fortunately, you don’t have to replace your printer. Instead, you can adjust the alignment of your existing printer.
How to Adjust Printer Alignment in Quickbooks
To adjust the alignment of your printer, you’ll need to access the “Print setup” feature in Quickbooks. You can find this feature in Quickbooks Online by logging in to your account and choosing “+ New,” followed by “Print Checks.” At the bottom of this screen is “Print setup.”
Upon clicking the “Print setup” button, choose “No, continue setup” at the bottom. You’ll need to click this link twice to initiate the adjustment feature. Next, click the grid and drag it to the square. The location of the grid inside the square will affect your printer’s adjustment. When you move the grid, Quickbooks will adjust your printer. Therefore, you should place the grid exactly inside the square for optimal adjustment.
Test Your Printer
After performing the adjustment described above, you can test your printer by printing a sample page. This is done by accessing “+ New” and choosing “Print Checks,” followed by “Print Setup” and then “View preview and print sample.” Ideally, the sample should come out of the printer aligned and without any unwanted distortion. With that said, you may need to adjust it one or more additional times.
If the sample is still misaligned, go back and perform another alignment using the steps mentioned above. Adjusting the alignment of a printer takes time. Whether you do it in Quickbooks or any other program — or even your computer’s operating system — you may have to perform several adjustments. Quickbooks makes it easy to perform these adjustments, however. Once you print a properly aligned sample page, click the option for “Finish Setup.”
In Conclusion
Depending on how your business operates, you may not need to use the print feature in Quickbooks. Many businesses are now paperless, meaning they use digital documents like email rather than paper documents. If your business uses paper documents, though, you’ll need to ensure they aren’t misaligned.
Did this tutorial work for you? Let us know in the comments section below!

What Are Accrued Expenses in Accounting?
 Accrued expenses are common when running a business. Whether your business operates in the B2B or B2C sector, it will probably face accrued expenses. As you buy products or services that are essential to your business’s operations, these expenses will generally increase. What are accrued expenses in accounting exactly, and how do they differ from other expenses?
Accrued expenses are common when running a business. Whether your business operates in the B2B or B2C sector, it will probably face accrued expenses. As you buy products or services that are essential to your business’s operations, these expenses will generally increase. What are accrued expenses in accounting exactly, and how do they differ from other expenses?
Overview of Accrued Expenses
Also known as accrued liabilities, accrued expenses are costs incurred by your business that have been recorded but not satisfied. Not all business-related purchases require upfront payment. If you’re buying a wholesale shipment of products to resell, for instance, the vendor may simply send you an invoice. Vendors often have strong relationships with their clients. As a result, many of them allow their clients to buy products or services on credit. When you make a purchase for your business, an accrued expense is created until you pay for it.
Accrued expenses are considered liabilities because they haven’t been satisfied. Using the same example from above, an accrued expense is created if you buy products from a vendor. You must wait for the vendor to send you an invoice, after which you must pay the total amount denoted on the invoice.
Accrued Expenses vs Accounts Payable: What’s the Difference?
While they are both considered liabilities, accrued expenses and accounts payable aren’t the same. Basically, accounts payable are short-term liabilities that require payment in the near future. Accrued expenses, on the other hand, are usually long-term liabilities that haven’t been recorded. Payment dates can vary, but most accrued expenses are considered long-term liabilities.
Don’t Forget to Record Accrued Expenses
Some business owners neglect to record accrued expenses. They assume that an expense shouldn’t be recorded until it is paid. Of course, this is a bad habit that can adversely affect your business’s financial records. If you don’t record an accrued expense, you won’t be able to fully realize your business’s true liabilities and, therefore, its cash flow.
When your business generates an accrued expense, its liabilities will increase. An accrued expense is a liability, and like all liabilities, you must pay them at a later date. As a result, it’s important to record your business’s accrued expenses. Regardless of its total cost, accrued expenses can affect your business’s cash flow. By recording them, you’ll have a clearer and more accurate representation of your business’s financial health.
Have anything else that you’d like to add? Let us know in the comments section below!

Comparing the 3 Types of Quickbooks Payroll Services
 With Quickbooks, you don’t have to manually pay your business’s employees each and every payday. You can take advantage of the accounting software’s payroll services. Quickbooks offers several payroll services that you can use to pay your business’s employees, including Core, Premium and Elite. What’s the difference between these three payroll services exactly?
With Quickbooks, you don’t have to manually pay your business’s employees each and every payday. You can take advantage of the accounting software’s payroll services. Quickbooks offers several payroll services that you can use to pay your business’s employees, including Core, Premium and Elite. What’s the difference between these three payroll services exactly?
#1) Core
In Quickbooks Online, Core is the lowest-tier payroll service. The Core payroll service comes with automated forms, automated taxed, automated payments to employees, support for employee health benefits and next-day direct deposits.
#2) Premium
A step up from Core is the Premium payroll service. It has all the same features as the Core payroll service but with a few extras. Rather than next-day direct deposits, for example, the Premium payroll service comes with same-day direct deposits. Other added featured in Quickbooks’s Premium payroll service include workers’ compensation administration, human resources (HR) support center, expert setup review and on-the-go time tracking.
#3) Elite
At the top of the payroll totem pole is Elite. It’s the most expensive payroll service available in Quickbooks Online. It has all the features of both the Core and Premium payroll services but with some added features that are particularly useful for large businesses. The Elite payroll service comes with a white-glove setup. This means Intuit’s customer service will help your business set up the Elite payroll service by walking you through the steps. The Elite payroll service also comes with tax penalty protection. This added feature lives up to its namesake by checking your business’s financial records for issues that could otherwise lead to a tax penalty.
What About Payroll for Quickbooks Desktop?
Core, Premium and Elite payroll services are only available in Quickbooks Online. Fortunately, there are similar payroll services available in Quickbooks Desktop. In Quickbooks Desktop, you can choose from Basic, Enhanced or Assisted payroll.
Basic payroll, of course, is the lowest-tier payroll service for Quickbooks Desktop. It comes with automated payments to employees, time-tracking integration, W-2 and 1099 setup and free direct deposits. The Enhanced payroll comes with about a half-dozen extra features, some of which include a workforce portal, free support, state and federal tax forms, electronic W-2 submissions and more. Finally, the Assisted payroll service comes includes job cost tracking, class tracking and support for up to 250 employees. You can learn more about the payroll services available in Quickbooks Desktop by clicking here.
Have anything else that you’d like to add? Let us know in the comments section below!

Items vs Expenses in Quickbooks: What’s the Difference?
 When using Quickbooks to keep track of your business’s finances, you’ll probably come across items and expenses. Quickbooks offers items and expenses to track costs incurred by your business. Items and expenses aren’t the same, however. They are designed for different purposes, and to use them correctly, you must learn the nuances between items and expenses.
When using Quickbooks to keep track of your business’s finances, you’ll probably come across items and expenses. Quickbooks offers items and expenses to track costs incurred by your business. Items and expenses aren’t the same, however. They are designed for different purposes, and to use them correctly, you must learn the nuances between items and expenses.
What Is an Item?
An item is any recorded product or service that your business purchases or sells. Quickbooks offers several item types, including service, inventory part, non-inventory part, other charge, subtotal, group, assembly and more. If your business buys or sells a product or service, you can record it as an item.
To create an item in Quickbooks, click the “Lists” menu and choose “Items.” You can then select the option for “Item,” followed by “New.” Quickbooks will prompt you to select the type of item you wish to create. Next, complete the fields for the item, after which you can click “Save” to complete the process.
What Is an Expense?
An expense is a cost incurred by your business. It may consist of anything from rent or lease payments, utilities, office supplies, legal fees, cleaning service and more. All businesses incur expenses. When you spend money on services such as these, you should record them as expenses. Quickbooks offers a separate area for recording expenses.
To create an expense in Quickbooks, click the (+) icon and select “Expense.” You can then enter information about the expense, such as the payee or vendor. You’ll also need to select a payment account with the date of purchase and payment method. After entering the required information, click “Save and close” or “Save and new.”
Comparing the Differences Between Items and Expenses
Items are used for any product or service that’s directly related to your business’s operations. If your business buys 100 units of a product to resell for a profit, you should record those product units as items. You’ll be reselling them in hopes of generating a profit, so they are considered items. Expenses, on the other hand, don’t affect your business’s revenue-generating capabilities. You’ll still have to pay for expenses — and in many cases expenses are essential to keeping businesses up and running — but you don’t resell or other turn expenses.
Another difference between items and expenses is that the former supports tracking. If your business operates from multiple locations, you can use items to track specific products or services sold from each location.
Have anything else that you’d like to add? Let us know in the comments section below!

How to Add a New Expense Category in Quickbooks
 Quickbooks supports the use of categories to organize transactions. Categories make it easier to track your business’s expenses. Rather than keeping all your expenses grouped together, for instance, you can split them up into relevant categories. Quickbooks doesn’t require the use categories, but leveraging this feature can make a world of difference in your financial accounting efforts. How do you add new expense categories in Quickbooks exactly?
Quickbooks supports the use of categories to organize transactions. Categories make it easier to track your business’s expenses. Rather than keeping all your expenses grouped together, for instance, you can split them up into relevant categories. Quickbooks doesn’t require the use categories, but leveraging this feature can make a world of difference in your financial accounting efforts. How do you add new expense categories in Quickbooks exactly?
Steps to Creating a New Expense Category
You can find the option to add new expense categories in your chart of accounts. To get started, log in to Quickbooks and click the “Accounting” menu, followed by “Chart of Accounts.” Next, click “New” in the top-right corner. You can then choose “Expense” or “Other Expense” under the “Account Type” option. When finished, select a detail type for the expense and enter a name for the new category. You’ll also see a field for number and description. To complete the process, click “Save and Close.”
Keep in mind, Quickbooks Self-Employed doesn’t support the creation of expense categories. If you use Quickbooks Self-Employed, you’ll have to choose from one of the software’s default categories.
How Expense Categories Work
Expense categories work by allowing you group similar transactions together. You can create categories for your business’s various products or services. Alternatively, you can create them for your business’s expenses. Categories are simply used for classification purposes. In Quickbooks, they allow you to group similar types of expenses together.
There’s really no wrong way to use expense categories as long it helps you track your business’s expenses. If you operate a retail store, for example, you may want to create an expense category for utilities and another expense category for inventory purchases. With these expense categories, you can quickly see how much money your business has spent on utilities and inventory over an extended period. Without expense categories, utilities and inventory would be grouped together, thereby making it difficult to distinguish between these two expenses.
In Conclusion
An expense category is a method by which you can group similar business-related expenses together in Quickbooks. Like other categories, Quickbooks doesn’t require them. Expense categories is an optional feature that won’t affect your business’s recorded transactions. Nonetheless, they can prove useful if your business has a lot of expenses, particularly different types of expenses.
Did this tutorial work for you? Let us know in the comments section below!

Quickbooks Now Supports Amazon Business Integration
 Amazon offers a convenient all-in-one platform for purchasing products and services. It doesn’t just cater to consumers, however. Amazon sells products and services to businesses as well. If you use Amazon Business, you’ll be pleased to hear that it now integrates directly with Quickbooks.
Amazon offers a convenient all-in-one platform for purchasing products and services. It doesn’t just cater to consumers, however. Amazon sells products and services to businesses as well. If you use Amazon Business, you’ll be pleased to hear that it now integrates directly with Quickbooks.
Intuit Announces Amazon Business Integration for Quickbooks Online
In September 2020, Intuit announced that its Quickbooks Online accounting software will support Amazon Business transactions. When integrated, Quickbooks Online will automatically pull all your transactions from Amazon Business.
“Small businesses are increasingly looking for ways to seamlessly manage their business, while reducing the time it takes to do so. This integration allows both small businesses, and the accountants who serve them, to better manage a business owners’ purchases and overall books,” said Intuit’s Rajneesh Gupta in a statement.
How to Set Up Amazon Business With Quickbooks Online
To set up Amazon Business with Quickbooks Online, log in to your Quickbooks account as admin and navigate to the Amazon Business Purchases app section. From here, click the option for “Get app now.” You will then be asked to log in to your Amazon Business account. Next, choose a start date for transaction imports. If you want to import all of your transactions from the current year, for example, set the start date to January 1. Click “Finish” to begin to the import.
After clicking “Finish,” Quickbooks Online will begin to import all of your Amazon transactions from the specified start date. Depending on how many transactions you have, it may take several minutes or longer. Keep in mind, Quickbooks will continue to check your Amazon account several times a day to see if you’ve made any additional transactions. If you buy a product on Amazon after setting up Amazon Business, Quickbooks will automatically update your records with the transaction.
Add Transactions
Once you’ve integrated Amazon Business with Quickbooks, you can add the transactions to your books. To do this, go to the “Banking” tab in Quickbooks and choose “App transactions,” followed by “For review.” You can then choose either “Add or Match” or “Review” for each listed transaction. The former option means the transaction is ready to be added to your books. The latter option places the selected transaction or transactions on hold so that you confirm them before adding them to your Chart of Accounts.
Have anything else that you’d like to add? Let us know in the comments section below!
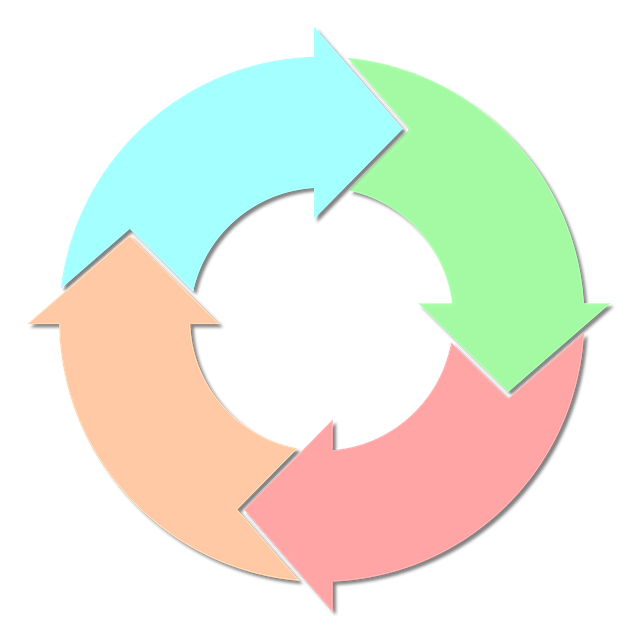
The 4 Steps of the Accounting Cycle
 Accounting is essential to running a successful business. If you don’t know how much money your business spends, as well as how much money it generates in sales revenue, you’ll struggle to create a profitable business. While there are different ways to approach accounting, one of the popular methods involves the four-step accounting cycle. In just four simple steps, you can keep track of your business’s financial information.
Accounting is essential to running a successful business. If you don’t know how much money your business spends, as well as how much money it generates in sales revenue, you’ll struggle to create a profitable business. While there are different ways to approach accounting, one of the popular methods involves the four-step accounting cycle. In just four simple steps, you can keep track of your business’s financial information.
#1) Analyze Transactions
The first step of the accounting cycle is to analyze transactions. Transactions may consist of receipts and invoices. Receipts, of course, denote an expense, whereas invoices denote revenue generated. To begin with the accounting cycle, you must identify all of your business’s transactions for the given financial period.
#2) Record Transactions
After analyzing your business’s transactions, you’ll need to record them in the form of journal entries. Journal entries are a form of structured data about transactions. They typically include the date of a transaction, the dollar amount of a transaction, the account number associated with the transaction and a brief description. If you use Quickbooks, you can create journal entries for your business’s transactions using the accounting software.
#3) Add Journal Entries to General Ledger
The third step of the accounting cycle is to add the newly created journal entries to your business’s general ledger. The general ledger is a document that contains journal entries for transactions. Also known as the nominal ledger, it serves as the central hub for accounting processes. You can review your business’s general ledger to gain a better understanding of its financial health. Once you’ve identified your business’s transactions and recorded them in the form of journal entries, you should add those journal entries to your business’s general ledger.
#4) Run an Unadjusted Trial Balance Report
The fourth and final step of the accounting cycle is to run an unadjusted trial balance report. What is an unadjusted trial balance report exactly? It’s a summary of all the balances in your business’s general ledger. With an unadjusted trial balance report, you’ll see an overview of your business’s transactions displayed neatly in a single report.
The accounting cycle may seem confusing, but it’s actually rather simple. It consists of four basic steps: analyze transactions, record transactions, add journal entries to the general ledger and run an unadjusted trial balance report.
Have anything else that you’d like to add? Let us know in the comments section below!

Estimates vs Quotes in Quickbooks: What’s the Difference?
 Quickbooks supports the creation of estimates and quotes. When selling products or services to your business’s customers, you may want to use one of these alternative pricing formats. Neither estimates nor quotes are fixed prices. Rather, they are used to help customers understand about how much money they can expect to pay for a product or service. To use them correctly, you’ll need to familiarize yourself with the differences between estimates and quotes.
Quickbooks supports the creation of estimates and quotes. When selling products or services to your business’s customers, you may want to use one of these alternative pricing formats. Neither estimates nor quotes are fixed prices. Rather, they are used to help customers understand about how much money they can expect to pay for a product or service. To use them correctly, you’ll need to familiarize yourself with the differences between estimates and quotes.
What Is an Estimate?
An estimate is a generalized prediction of how much a product or service will cost. It’s typically used when a business, such as a service contractor, has limited information about a customer’s project. If a customer requests a service, and the price of that service can vary depending on factors that are unknown at the time, you may want to give him or her an estimate.
The actual price of a customer’s project can change after he or she receives an estimate. If you discover that the project requires more labor or materials, you may need to charge the customer more. If the cost of the project is less than what you originally estimated, you may want to change the customer less. Regardless, an estimate is simply a prediction of how much money a customer can expect to pay.
What Is a Quote?
A quote, on the other hand, is a more detailed prediction of how much a product or service will cost. Like estimates, quotes aren’t set in stone. They are used to help customers understand how much money they can expect to pay for a project. With that said, quotes are usually more accurate than estimates.
When businesses create a quote, they evaluate the specific needs of the customer. Estimates are often created without looking at the customer’s needs. A business may create an estimate by using data from its past customers. To create a quote, businesses look at the details of a customer’s project to create a more accurate prediction of the actual cost.
In addition to estimates and quotes, Quickbooks supports the creation of proposals. A proposal is a document that breaks down all the costs associated with a customer’s project. Proposals are the most accurate in terms of pricing. When given to a customer, the customer can either accept or reject the proposal. If accepted, the proposal becomes binding.
Have anything else that you’d like to add? Let us know in the comments section below!
